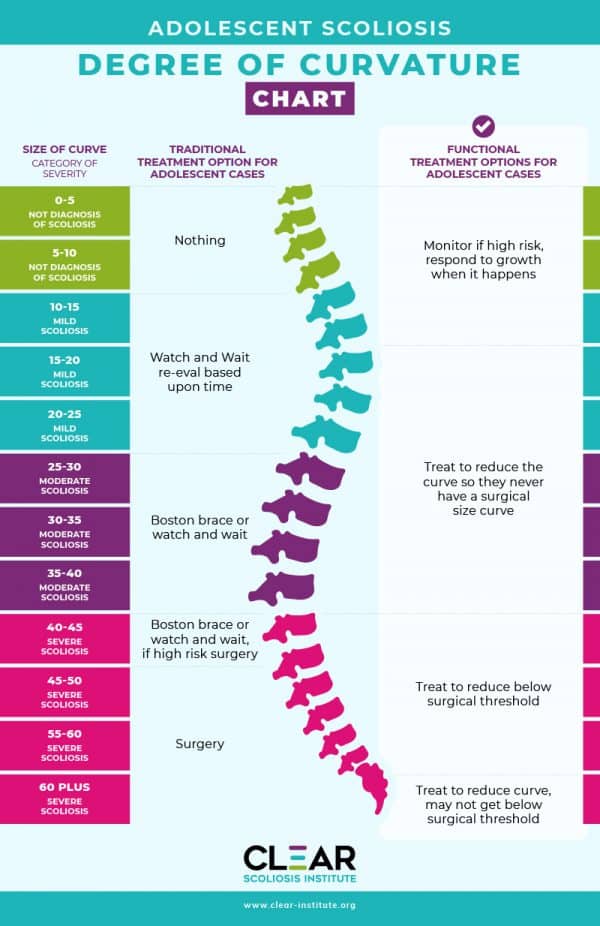
Scoliosis Degree Chart
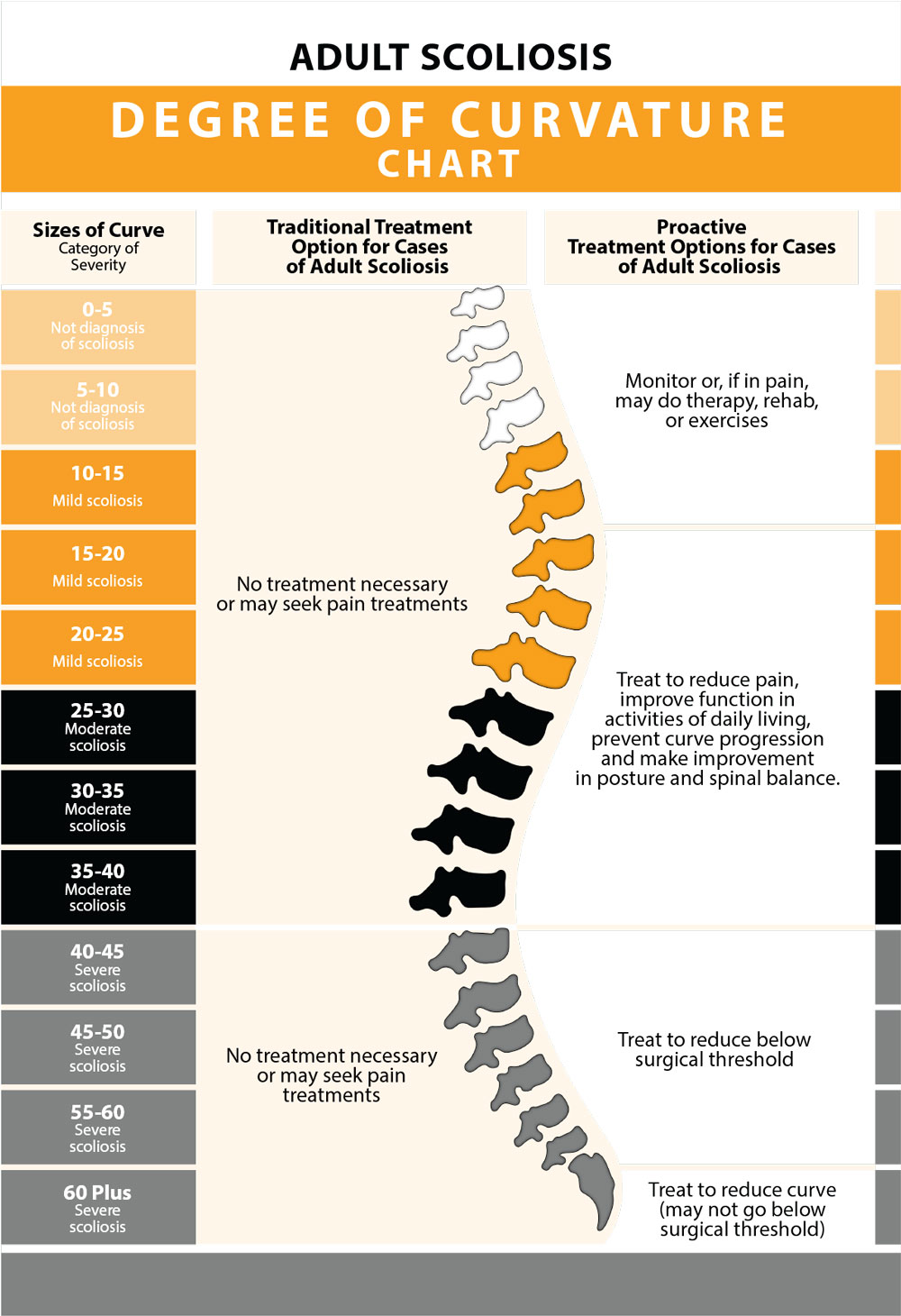
Scoliosis Degree Chart - Both the thoracic (mid) and lumbar (lower) spine may be affected by scoliosis. Web this chart not only provides vital insights into the severity of the condition but also plays a crucial role in guiding the treatment plan. What are the types of scoliosis? The upper cervical curve is convex forwards and is the reverse of the lower cervical curve. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (ais) degenerative scoliosis (de novo scoliosis) neuromuscular scoliosis. What are the degrees of curvature? They’ll rate the severity based on the degree of the curve: Web the scoliosis degrees of curvature chart is a crucial tool for assessing and managing scoliosis. How is adult scoliosis diagnosed? Cobb angle measurements between 25 and 40 degrees are diagnosed as moderate scoliosis, and 40+ degrees is classified as severe, while 80+ is considered very severe. Web a cobb angle of 10 degrees. What are the types of scoliosis? Scoliosis is a lateral (or sideways) curvature of the spine in one or more places. While scoliosis can occur in people with conditions such as cerebral palsy and muscular dystrophy, the cause of most childhood scoliosis is not known. Web the scoliosis degrees of curvature chart is a crucial tool for assessing and managing scoliosis. Both the thoracic (mid) and lumbar (lower) spine may be affected by scoliosis. Web table of contents. Spinal curvature from scoliosis may occur on the right or left side of the spine, or on both sides in different sections. 2 normally occurring curves in the cervical spine: Viewed from the back, a typical spine is straight. Between 10 to 24 degrees. Follow along on the accompanying scoliosis degrees chart for a visual of how the traditional and functional treatment approaches address the various severity levels. What sets the different types of scoliosis apart? The upper cervical curve is convex forwards and is the reverse of the lower cervical curve. 2 normally occurring curves in the cervical. The upper cervical curve extending from the occiput to the axis, and the longer lordotic curve of the lower cervical spine extending from the axis to the second thoracic vertebrae. Web here is a general outline of cobb angle ranges and what they could indicate in idiopathic scoliosis found in children and adolescents: Web adolescent idiopathic scoliosis is a lateral. Here's what you need to know about scoliosis, including the symptoms, causes, and treatments. Web table of contents. 2 normally occurring curves in the cervical spine: What sets the different types of scoliosis apart? In this comprehensive article, we will explore the scoliosis degrees of curvature chart in detail, offering you a clearer roadmap through the scoliosis journey. Scoliosis is diagnosed when the cobb angle reaches 10 degrees or more. Follow along on the accompanying scoliosis degrees chart for a visual of how the traditional and functional treatment approaches address the various severity levels. Web what part of the spine curves? Web cobb angle measurements between 10 and 25 degrees are classified as mild scoliosis; Scoliosis is not. Web cobb angle measurements between 10 and 25 degrees are classified as mild scoliosis; What are the degrees of curvature? What are the symptoms in adults? How is scoliosis in adults treated? The upper cervical curve is convex forwards and is the reverse of the lower cervical curve. Web this chart not only provides vital insights into the severity of the condition but also plays a crucial role in guiding the treatment plan. Below are seven types of scoliosis in greater detail: Web there are two main scoliosis treatment approaches for patients to choose between, each offering a different potential outcome; Between 10 to 24 degrees. Scoliosis is. Web scoliosis is an abnormal sideways curvature of the spine that also twists abnormally. What are the symptoms in adults? Scoliosis is a type of spinal deformity. Below are seven types of scoliosis in greater detail: Scoliosis is a lateral (or sideways) curvature of the spine in one or more places. Web this chart not only provides vital insights into the severity of the condition but also plays a crucial role in guiding the treatment plan. Spinal curvature from scoliosis may occur on the right or left side of the spine, or on both sides in different sections. What are the symptoms in adults? Below are seven types of scoliosis in. Web there are two main scoliosis treatment approaches for patients to choose between, each offering a different potential outcome; 2 normally occurring curves in the cervical spine: Between 10 to 24 degrees. What sets the different types of scoliosis apart? Web this chart not only provides vital insights into the severity of the condition but also plays a crucial role. Web a healthcare provider will measure the curve of your spine in degrees. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (ais) degenerative scoliosis (de novo scoliosis) neuromuscular scoliosis. Factors such as age, symptoms, and treatment options vary depending on the degree of curvature. Scoliosis is a lateral (or sideways) curvature of the spine in one or more places. Scoliosis is a sideways curvature of. What are the types of scoliosis? Web scoliosis is an abnormal sideways curvature of the spine that also twists abnormally. Web what part of the spine curves? Web here is a general outline of cobb angle ranges and what they could indicate in idiopathic scoliosis found in children and adolescents: Web the scoliosis degrees of curvature chart is a crucial tool for assessing and managing scoliosis. Follow along on the accompanying scoliosis degrees chart for a visual of how the traditional and functional treatment approaches address the various severity levels. Scoliosis is a lateral (or sideways) curvature of the spine in one or more places. It is the most common form of. Web take a look at the accompanying scoliosis degrees of curvature chart for both adolescents and adults, to see how each of the two main scoliosis treatment approaches responds at each severity level; In about 80% of cases, the scoliosis is considered idiopathic (without a congenital or other underlying cause). It is a term used to describe any abnormal, lateral (sideways) curvature of the spine. Factors such as age, symptoms, and treatment options vary depending on the degree of curvature. Scoliosis is diagnosed when the cobb angle reaches 10 degrees or more. Spinal curvature from scoliosis may occur on the right or left side of the spine, or on both sides in different sections. What sets the different types of scoliosis apart? Both the thoracic (mid) and lumbar (lower) spine may be affected by scoliosis.Scoliosis Degrees Of Curvature Chart
What Is Scoliosis? A Comprehensive Overview
Exploring The Scoliosis Degrees Of Curvature Chart
Scoliosis Degrees Of Curvature Chart
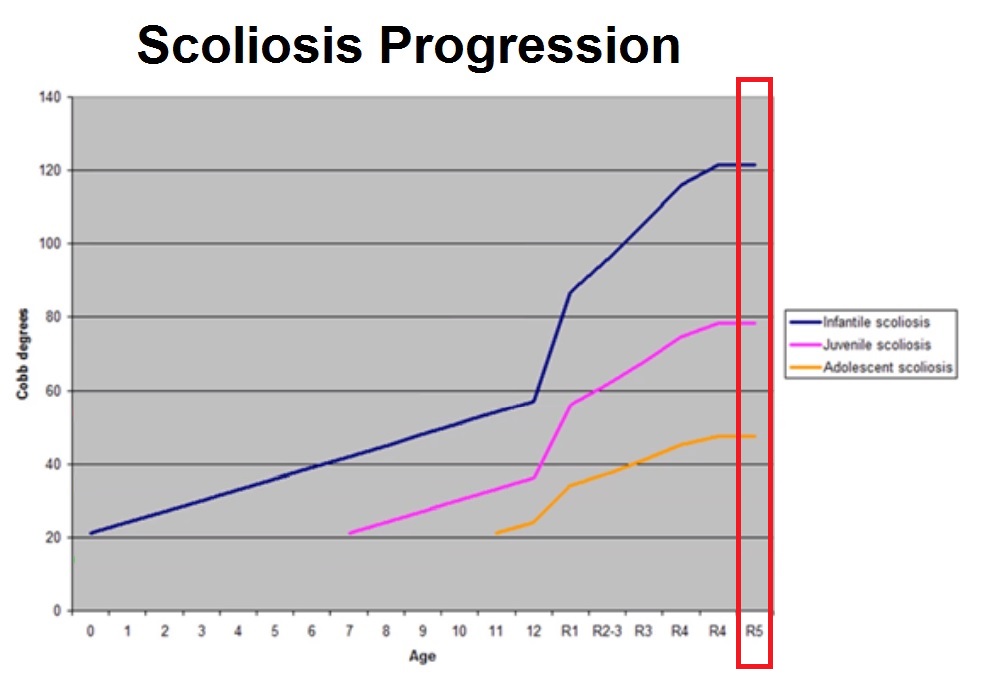
Scoliosis Progression Chart Simplified Treating Scoliosis
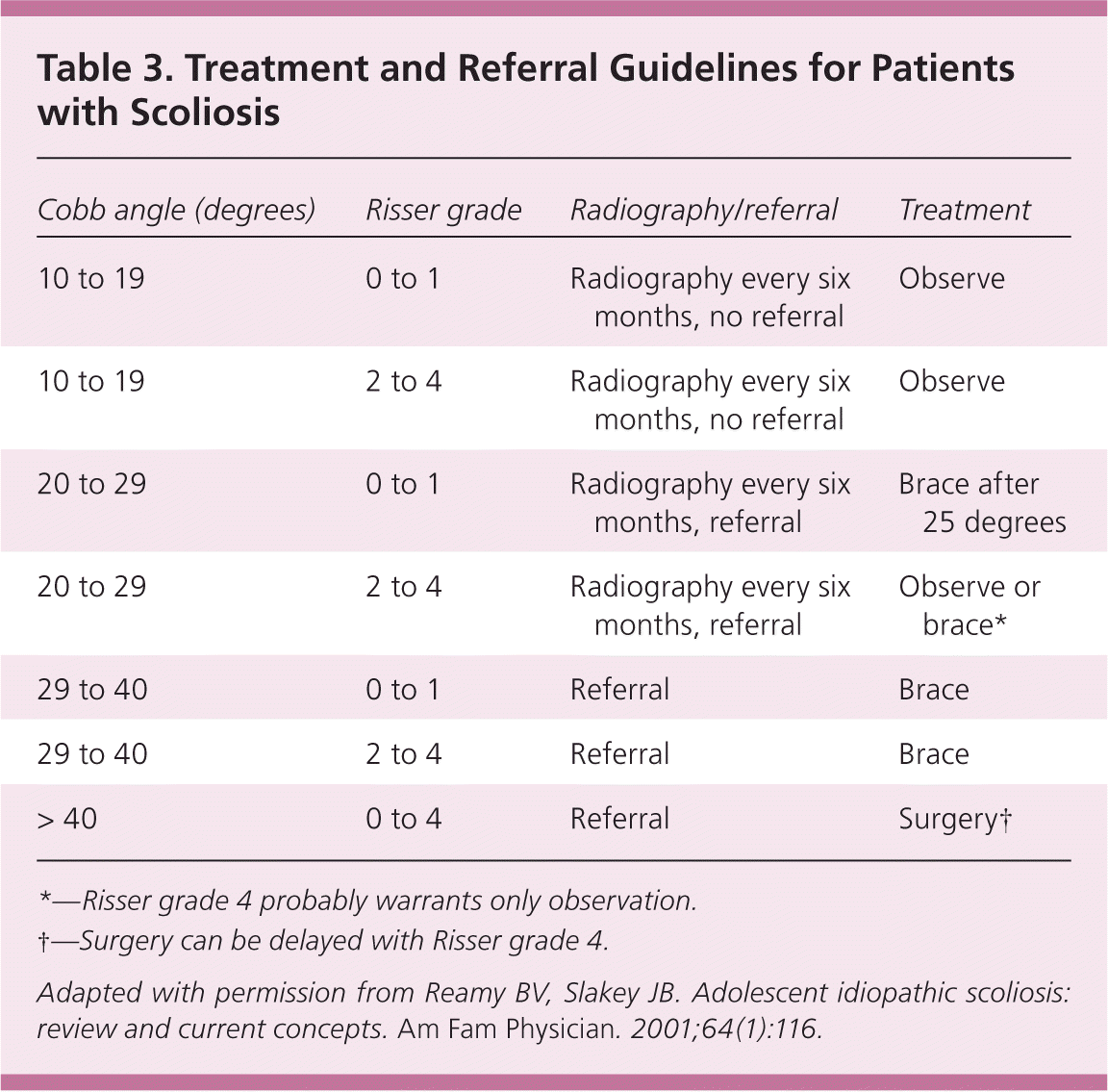
Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Diagnosis and Management AAFP
Scoliosis Degrees Of Curvature Chart
Scoliosis Progression
Dive Into the Scoliosis Degrees of Curvature Chart Advanced Spine
Extent, types and stages of scoliosis, their classification
Scoliosis Is Not A Disease.
Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (Ais) Degenerative Scoliosis (De Novo Scoliosis) Neuromuscular Scoliosis.
Web Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Is A Lateral Curvature Of The Spine (I.e., The Cobb Angle) Of 10 Degrees Or More That Affects Adolescents 10 To 18 Years Of Age.
Web The Degrees Of Curvature Chart Categorizes The Severity Of Scoliosis By Assigning A Degree Of Curvature Number.
Related Post: