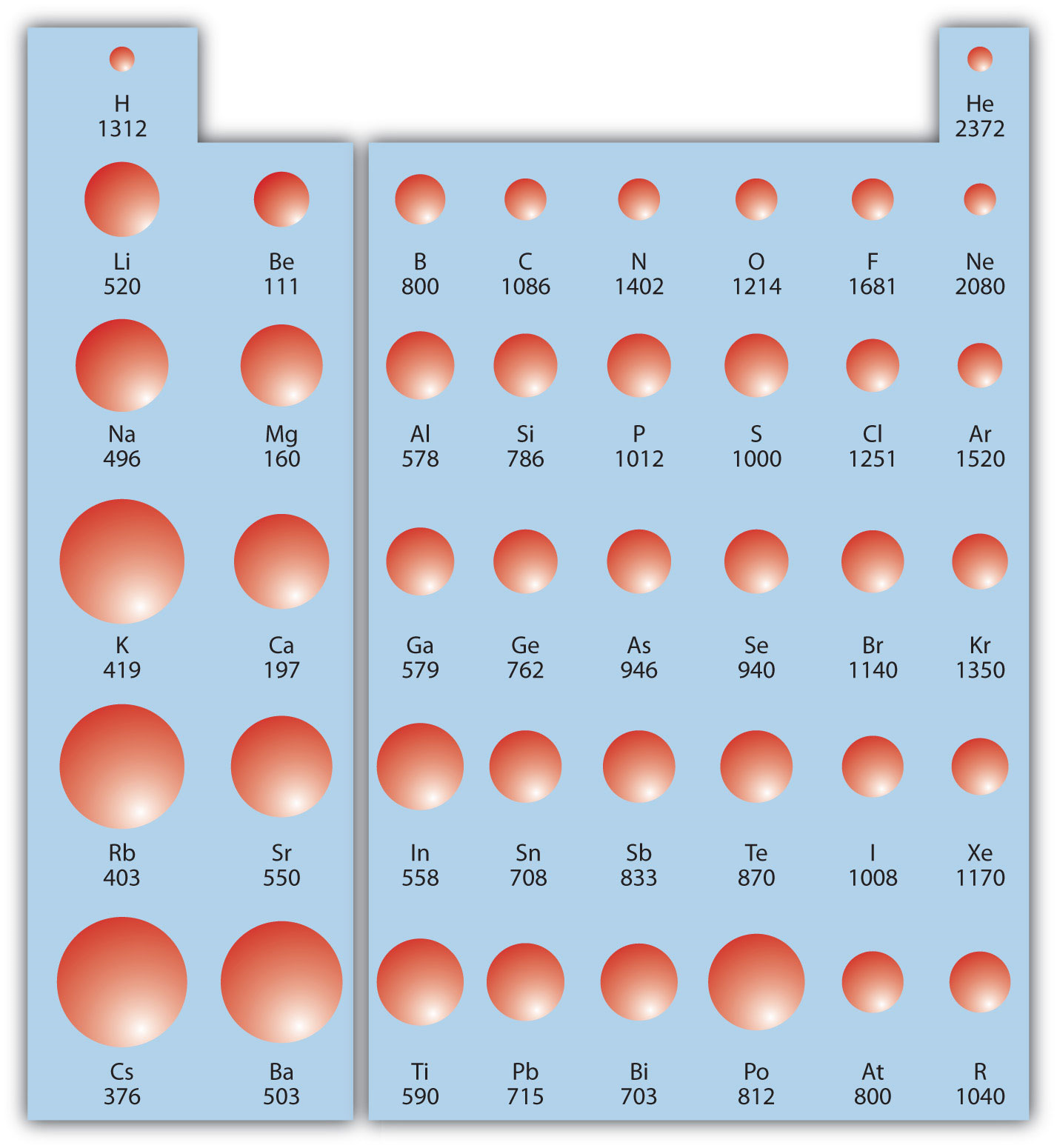
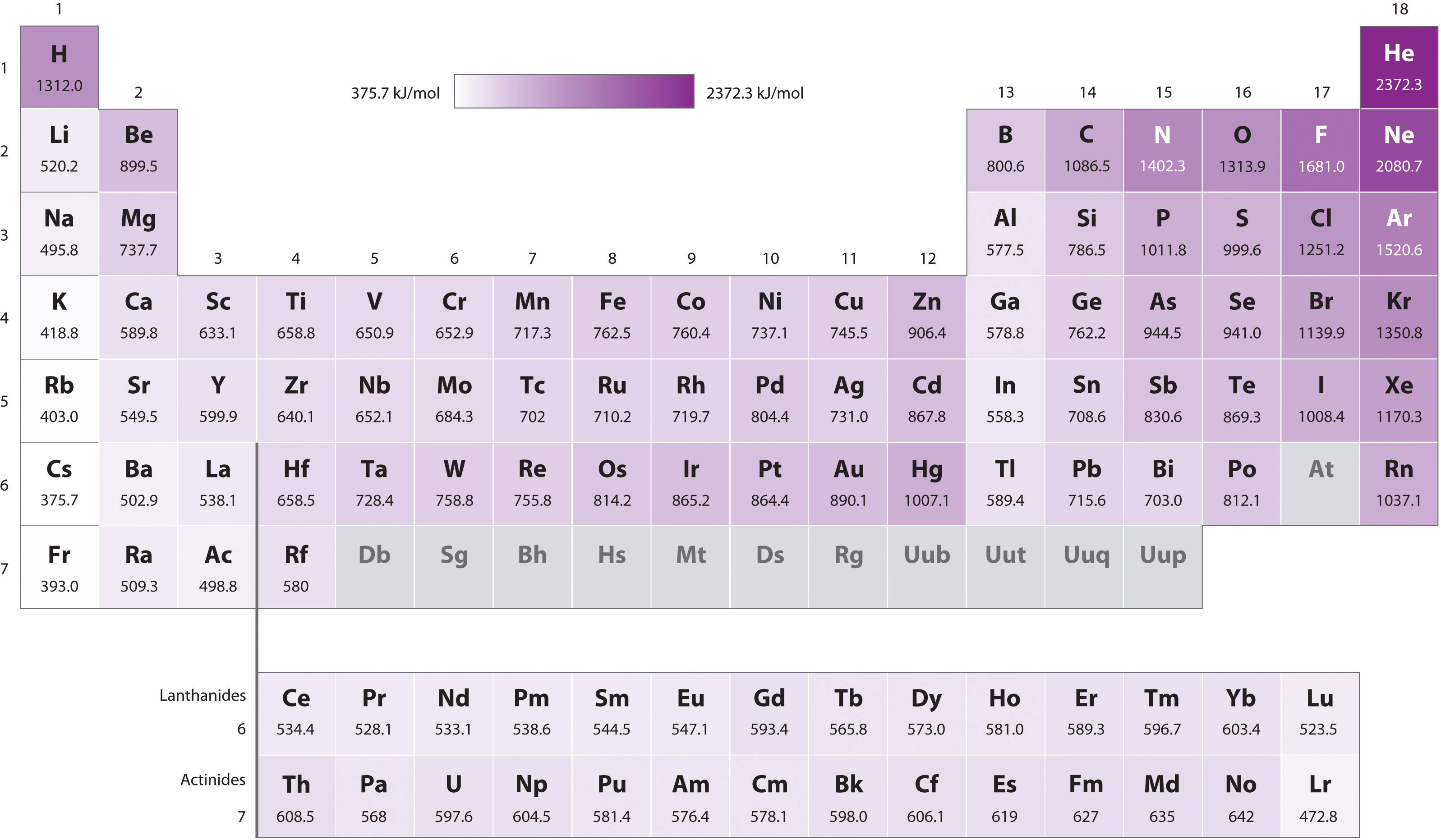
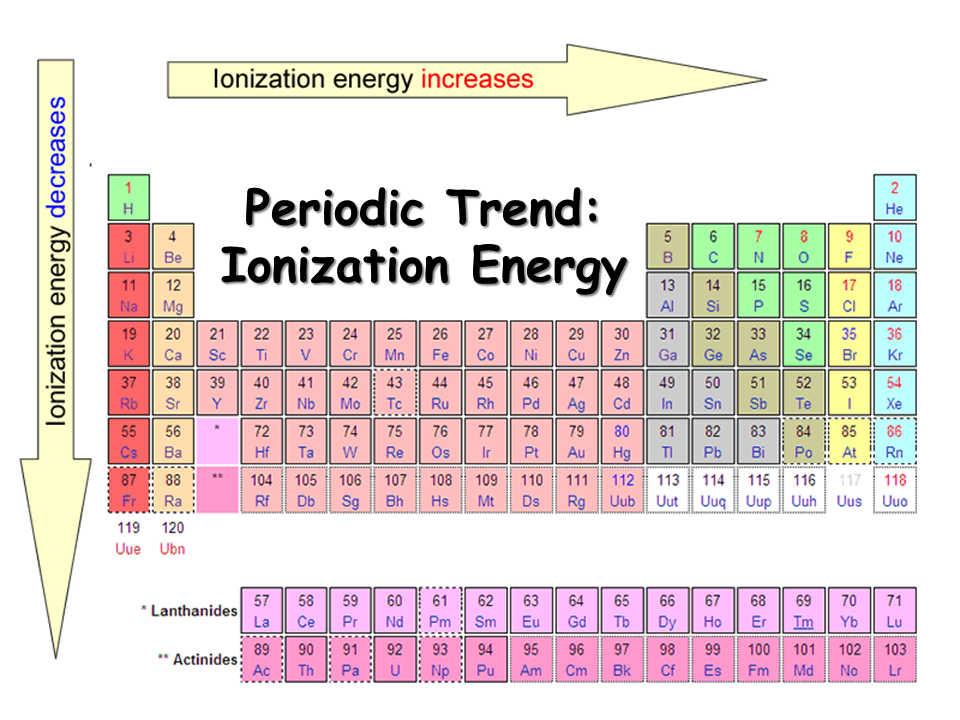
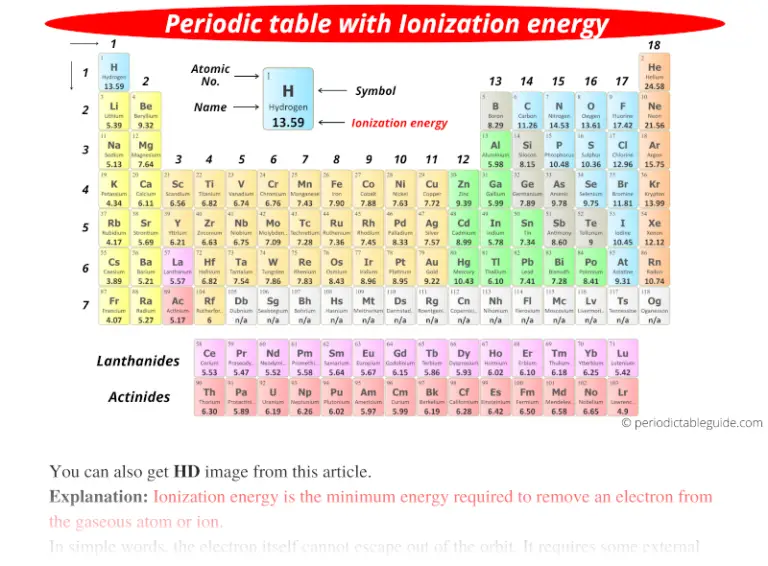
Ionisation Energy Chart
Ionisation Energy Chart - The table lists only the first ie in ev units. Web the 1st ionization energy of the element m is a measure of the energy required to remove one electron from one mole of the gaseous atoms m. \(i\) is therefore the energy required for the reaction Web ionization energy (the energy associated with forming a cation) decreases down a group and mostly increases across a period because it is easier to remove an electron from a larger, higher energy orbital. To convert to kj/mol, multiply by 96.4869. Web ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from a neutral atom in its gaseous phase. Ionization energy is always positive. 1st in a periodic table cityscape style. Learn its chemical equation, values, trends across a period & down a group, & exception. A high value of ionization energy shows a high attraction between the electron and the nucleus. The energy required to remove an electron is the ionization energy. The ionization energy differs for each atom. To convert to kj/mol, multiply by 96.4869. First ionization energy, second ionization energy as well as third ionization energy of the elements are given in this chart. Web what is ionization energy? Web first ionization energy (kj/mol) Nist reference table on ground states and ionization energies for the neutral atoms. Web explore how ionization energy changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. Web these tables list values of molar ionization energies, measured in kj⋅mol −1. Web ionization is the process of removing an electron from a neutral atom (or compound). The measurement is performed in the gas phase on single atoms. Web ionization energy chart of all the elements is given below. To convert to kj/mol, multiply by 96.4869. Web ionization energy is a measure of the energy needed to pull a particular electron away from the attraction of the nucleus. Web one is that when electrons start to fill. Web ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from a neutral atom in its gaseous phase. Web complete and detailed technical data about the element $$$elementname$$$ in the periodic table. As described above, ionization energies are dependent upon the atomic radius. Web these tables list values of molar ionization energies, measured in kj⋅mol −1. The energy required. Web ionization energies of the elements. Another is when each of 3 p orbitals have one electron they start to pair as new ones are added (like when moving from nitrogen to oxygen). Web what is ionization energy? First ionization energy, second ionization energy as well as third ionization energy of the elements are given in this chart. Web complete. Another is when each of 3 p orbitals have one electron they start to pair as new ones are added (like when moving from nitrogen to oxygen). The ionization energy of the elements within a period. The ionization energy differs for each atom. Web explore how ionization energy changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive. Web complete and detailed technical data about the element $$$elementname$$$ in the periodic table. 1st in a periodic table cityscape style. Web ionization energy chart of all the elements is given below. Web periodic table and trend of ionization energies. Web these tables list values of molar ionization energies, measured in kj⋅mol −1. Web an element's first ionization energy is the energy required to remove the outermost, or least bound, electron from a neutral atom of the element. Web ionization energies of the elements. First ionization energy, second ionization energy as well as third ionization energy of the elements are given in this chart. \(i\) is therefore the energy required for the reaction. The stronger an electron is bound to an atom the more ionization energy it requires, therefore these two are directly proportional. A high value of ionization energy shows a high attraction between the electron and the nucleus. Web ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from a neutral atom in its gaseous phase. First ionization energy, second. Web ionization energies of the elements. Since going from right to left on the periodic table, the atomic radius increases, and the ionization energy increases from left to right in the periods and up the groups. Web the ionization energy of atoms, denoted e i, is measured by finding the minimal energy of light quanta or electrons accelerated to a. Also, learn first & second ionization energies. Web the ionization energy of atoms, denoted e i, is measured by finding the minimal energy of light quanta or electrons accelerated to a known energy that will kick out the least bound atomic electrons. Web ionization energies of the elements. The first molar ionization energy applies to the neutral atoms. Web an. Web ionization energies of the elements. Web ionization energy is the amount of energy needed to remove an electron from a neutral gaseous atom and form an ion. Ionization energy is always positive. Also, learn first & second ionization energies. The table lists only the first ie in ev units. There are trends that match the structure of the periodic table. Another is when each of 3 p orbitals have one electron they start to pair as new ones are added (like when moving from nitrogen to oxygen). Learn the definition, trend on the periodic table, first & second ionization energies, see a chart and much more. Also, learn first & second ionization energies. First ionization energy, second ionization energy as well as third ionization energy of the elements are given in this chart. The energy required to remove an electron is the ionization energy. Web ionization energy is the amount of energy needed to remove an electron from a neutral gaseous atom and form an ion. Image showing periodicity of the chemical elements for ionization energy: The first molar ionization energy applies to the neutral atoms. Web complete and detailed technical data about the element $$$elementname$$$ in the periodic table. Other values are molar ionization energies given in the unit kj/mol. The first of these quantities is used in atomic physics, the second in chemistry, but both refer to the same basic property of the element. Web these tables list values of molar ionization energies, measured in kj⋅mol −1. Web ionization energy (the energy associated with forming a cation) decreases down a group and mostly increases across a period because it is easier to remove an electron from a larger, higher energy orbital. Web chemists define the ionization energy (\(i\)) of an element as the amount of energy needed to remove an electron from the gaseous atom \(e\) in its ground state. Web first ionization energy (kj/mol)Among the Following Which Element Has the Lowest Ionization Energy
9.9 Periodic Trends Atomic Size, Ionization Energy, and Metallic
Ionization Energy Chart Periodic Table
Periodic Trends in Ionization Energy CK12 Foundation
8.4 Ionization Energy Chemistry LibreTexts
Pin by Cristina Baldacci on Chemistry Education Chemistry education
Ionization Enthalpy NEET Lab
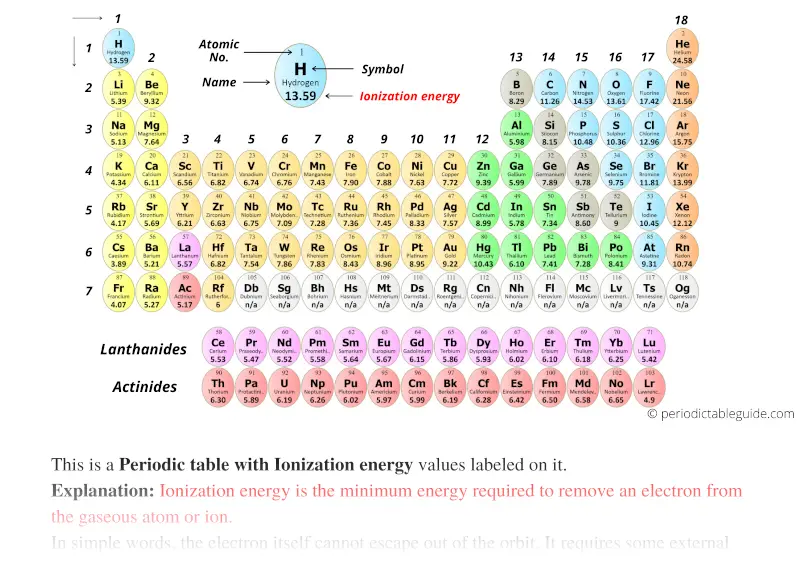
Periodic table with Ionization Energy Values (Labeled Image)
Periodic table with Ionization Energy Values (Labeled Image)
The Parts of the Periodic Table
Nist Reference Table On Ground States And Ionization Energies For The Neutral Atoms.
Web The Ionization Energy Of Atoms, Denoted E I, Is Measured By Finding The Minimal Energy Of Light Quanta Or Electrons Accelerated To A Known Energy That Will Kick Out The Least Bound Atomic Electrons.
Up To Date, Curated Data Provided By Mathematica 'S Elementdata Function From Wolfram Research, Inc.
\(I\) Is Therefore The Energy Required For The Reaction
Related Post: